MySQL vs. PostgreSQL: which one is the best

MySQL and PostgreSQL are currently the most commonly used open-source relational database management systems. In this article, you’ll learn about the key features of MySQL and PostgreSQL database systems. We’ll discuss what’s new for these two systems in 2019 and outline key technical differences. Read on to see the pros and cons of each system and some use cases. This article is geared towards database developers and Information Technology (IT) professionals.

MySQL vs. PostgreSQL:
After nearly 40 years, Relational Database Management Systems (RDBMS) continue to be the preferred method for storing and managing data. While today there are other data models such as NoSQL and NewSQL, the relational database model continues to dominate the market.
The most widely used open-source RDBMS are MySQL and PostgreSQL. In this article, we will compare their features to help you choose the right RDBMS for your company.
What is MySQL?
The most widely used open-source RDBMS, MySQL was designed with speed and functionality in mind. Is easy to install and offers flexibility. Oracle acquisition of MySQL provides lifetime technical support and advanced features in their enterprise edition.

Key Features
- Server available in a client-server model or embedded database
- Runs in Windows, Linux, and FreeBSD
- Multi-layered design
- Features built-in tools for query analysis
- Partially SQL compliant
- Open source under GNU license
- Supports C family languages, Perl, Node.js and PHP
What’s New for 2019 for MySQL
In April 2019 a new version of the MySQL Shell was released, which included the following features:
- Addition of a reporting framework.
- API to register custom reports.
- Shell command to display a specific report (\show).
- Shell command to monitor a specific report (\watch).
What is PostgreSQL?
This RDBMS is considered to be the most advanced and powerful open-source RDBMS. Is designed to perform complex queries and deal with large amounts of data. They were the first to introduce multi-version currency control (MVCC) that allows several users to read and write in the database at the same time.

Key Features
- Highest SQL standard compliance
- Extensible
- High concurrency
- ACID compliance (Atomicity, Consistency, Isolation, Durability)
- Object-related
- Open source through a proprietary license.
- Runs in Windows, Linux, X, and Unix.
- Supports C family languages, Delphi, JavaScript, Phyton, R, Go and .Net
What’s New for PostgreSQL
In May 2019, PostgreSQL 12 beta 1 was released with the following new and improved features:
- Improvements to the space management of standard B-tree indexes
- Reduction of index size for frequently modified B-tree indexes.
- A new ability allows rebuilding indexes concurrently.
- Executes JSON path queries according to the SQL/JSON specification in the SQL:2016 standard.
Key Technical Differences
Database Structure
Both systems are relational databases, and as such share more or less the same structure.
However, they do differ in their approach.
- PostgreSQL
An object-relational database that focuses on standard compliance and extensibility. The core components of the database are tables, constraints, triggers, roles, stored procedures and views. PostgreSQL identifies each row in a table by using primary keys. It also supports many NoSQL features.
- MySQL
A relational database that uses tables, constraints, triggers, and roles. However, MySQL emphasizes functionality rather than compliance. The newer versions of MySQL also support some NoSQL features.
Performance
Indexes allow the server to find and retrieve specific data without having to search through the entire table.
- PostgreSQL
Includes built-in support for standard B-tree indexes. In addition, it supports partial indexes, which lets it index only part of a table; it can also create an index from the result of a function.
- MySQL
Stores most indexes in B-trees, the exception being spatial data types that use R-trees. In addition, MySQL supports full-text indexes.
Replication
Replication is a process that allows data to be copied automatically between databases. Usually, there are “master” and “slave” databases, but some systems also allow you to copy from “master” to “master”.
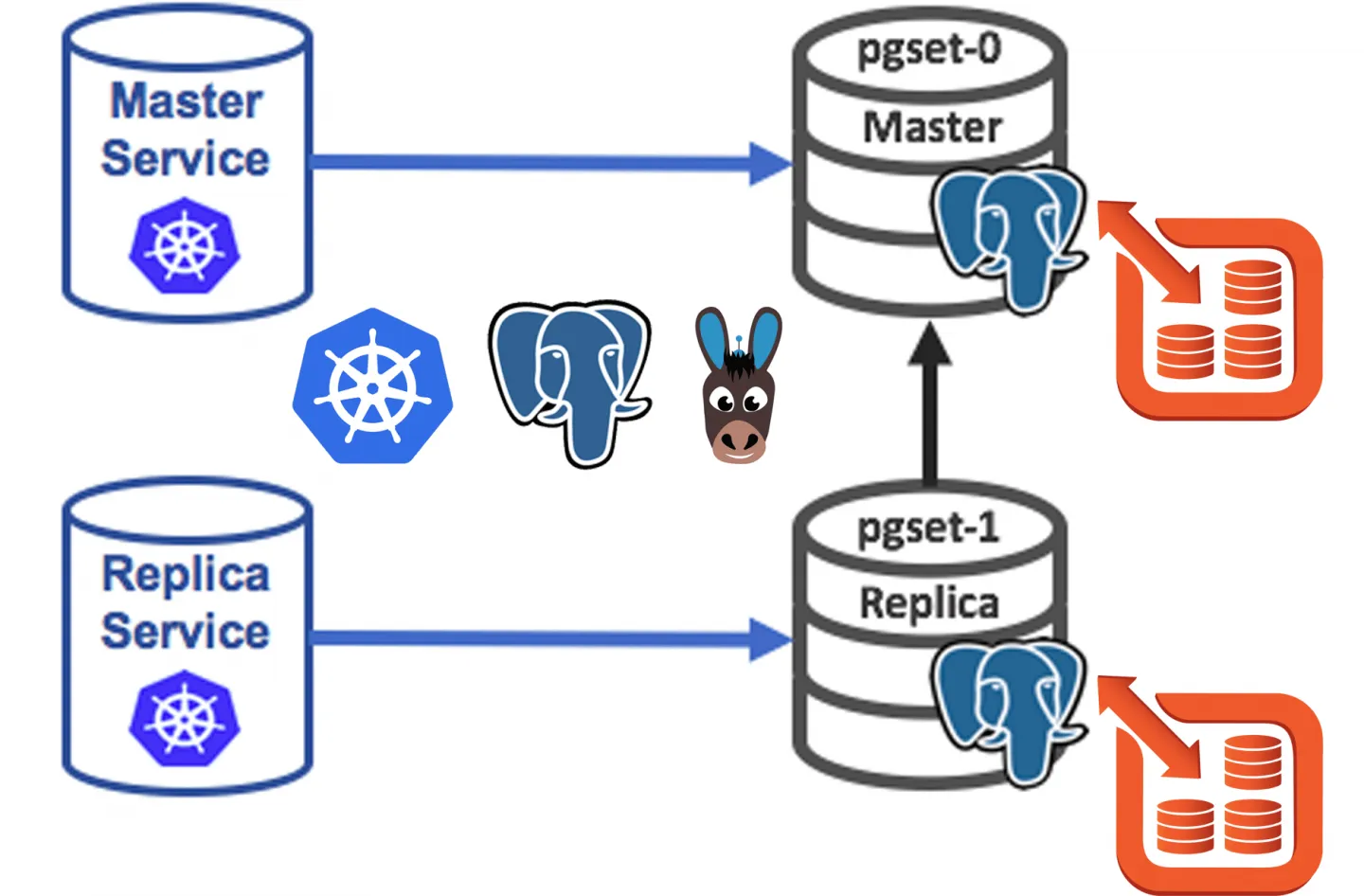
- PostgreSQL
Performs master-slave replication, using two databases running at the same time synchronizing the master database with the slave database. This method is called 2 safe synchronous replication.
- MySQL
Performs master-slave replication where one server acts as a master and the others as slaves.
Through MySQL Cluster, uses synchronous replication in a two-phase confirmation process to write the data in multiple servers.
Community Support
- PostgreSQL
Has a large and proactive community of users who regularly release feature improvements. The community support includes forums and mailing lists. Several companies also offer commercial support.
- MySQL
While the MySQL community has been around for longer, the users typically focus on maintaining existing features. This database offers many community support options in MySQL.com as well as commercial support via Oracle. The database giant provides support 24/7, unlimited support for incidents, and remote troubleshooting for MySQL enterprise users.
Administration Tools
- PostgreSQL
There are several tools you can use to deal with postgreSQL admin activities such as role management, backup and restore; and tablespace management.
- MySQL
MySQL uses Workbench to integrate database administration tools into a visual console. In addition, there are several other commercial administration solutions, which strive to improve the functionality in SQL queries and web administration.
Pros and Cons
MySQL
|
Advantages |
Disadvantages |
|
Easy to use. |
Lacks support for FULL JOIN clauses. |
|
Abundant documentation. |
Some features are only available through paid versions. |
|
A built-in security tool that supports user management and lets it grant privileges on a user basis. |
The development is slow, as the community focuses primarily on maintaining existing features. |
|
Supports different types of replication including horizontal scaling. |
|
PostgreSQL
|
Advantages |
Disadvantages |
|
High SQL compliance. Supports 160 of the 179 features required to full SQL:2011 compliance. |
Each database process gets about 10MB of memory. This result in large memory requirements for databases with many connections. |
|
The community releases new features periodically. In addition, there are several online resources for new users, including Postgresql wiki and online forums. |
Still not as popular as MySQL, as such fewer third-party tools are compatible with PostgreSQL. |
|
The catalog-driven operation ensure that the database is easily extensible and can readily meet the needs of the user, |
Use Cases
PostgreSQL:
- Data integrity— companies that need their data to remain consistent can benefit from the system MVCC feature.
- High Integration—is compatible with a lot of programming languages and operating systems which makes for easy integration with an array of tools.
- Complex queries—supports operations like data warehousing and online transaction processing.
MySQL:
- Websites—and web applications benefit from MySQL easy installation.
- Expansion needs—companies that require automatic sharding can benefit from MySQL commercial versions.
The Bottom Line
Nowadays, PostgreSQL and MySQL are the two most widely used open-source RDBMS.
While each has its strengths and limitations, a company should base their decision on their unique requirements. Although PostgreSQL is becoming more popular, MySQL is still on the lead with their Oracle supported development.





